WHAT IS A FULL STACK DEVELOPER? CONSIDERATIONS WHEN ASPIRING TO BECOME A FULL STACK DEVELOPER
According to the latest Stack Overflow Developer survey, Full-Stack Web Development remains the most popular trend today. It's no surprise that there are numerous online and offline training programs aimed at helping programmers become Full Stack Developers. These programs not only support newcomers in obtaining high-paying programming jobs but also provide assistance in achieving this goal.
In this article, I will provide guidelines for acquiring the most crucial skills needed to become a Full-Stack Web Developer.
1. What is a Full Stack Developer?
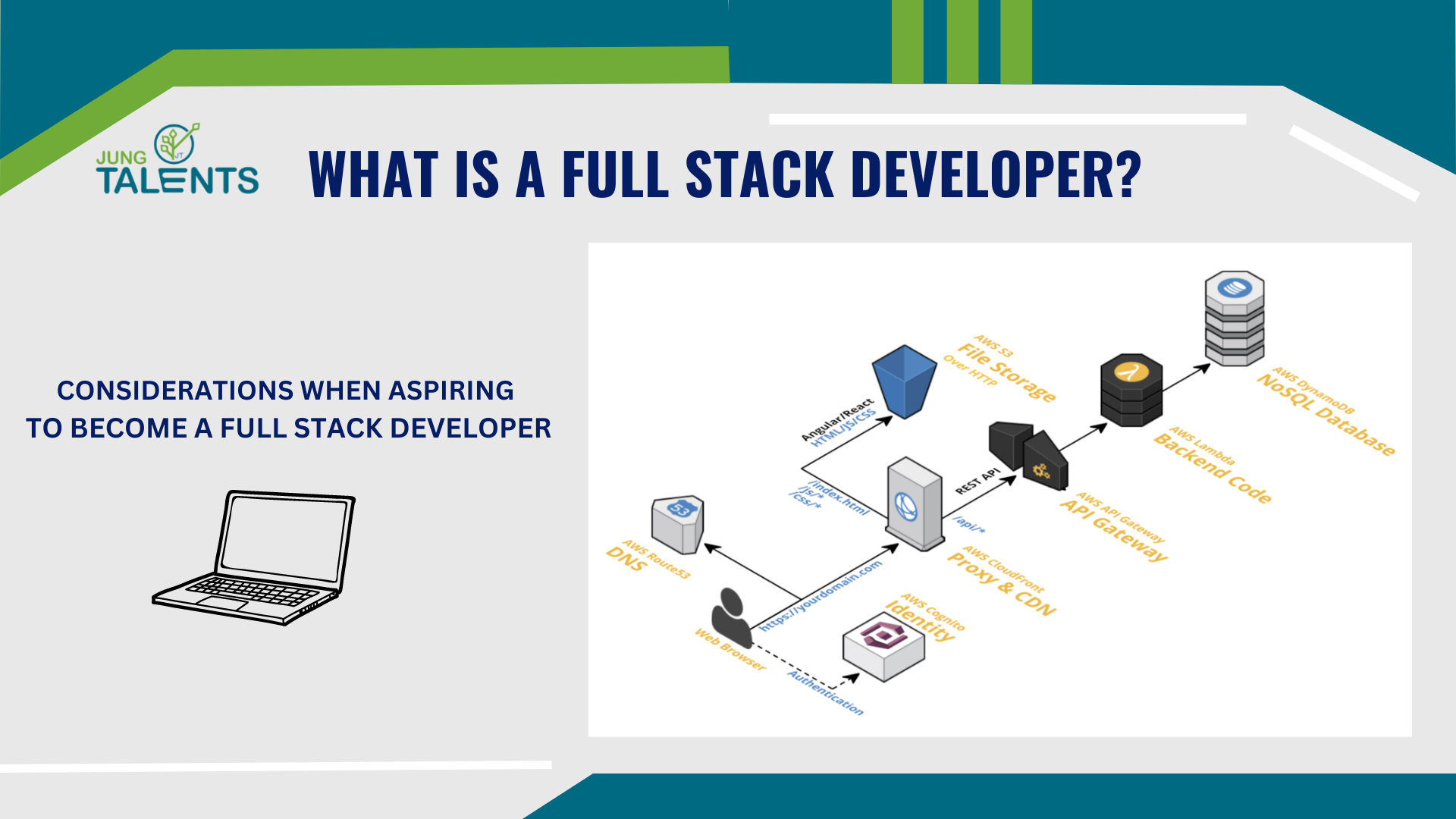
A Full-Stack Developer is someone who possesses a comprehensive understanding of both front-end and back-end aspects, along with deep knowledge of best practices and concepts. Naturally, Full Stack Developers can code for all components of a system and excel at it if they are truly skilled. This demands a broad range of skills and experience.
2. Roles and Responsibilities of a Full Stack Developer
A Full-Stack Web Developer is capable of working on both the front-end and back-end of an application. Front-end is generally the part visible and interactive to users, while back-end handles logic processing, database interaction, user authentication, server configuration, etc.
However, it's important to note that a Full Stack Developer's front-end work may not match that of a specialized front-end expert, and the same applies to the back-end. Full Stack Developers possess a broad understanding of various components and their interactions during development, ultimately combining them to create a complete product.
As a Full-Stack Web Developer, you aren't required to excel at every task from front-end to back-end, but you should be capable of working on both fronts and understanding the overall application development process.
If you aim to become a Full-Stack Web Developer or plan to embark on this career path, the following is a reference list of topics IT enthusiasts should learn:
2.1. HTML/CSS

Most online and offline Full-Stack Web Developer programs start with HTML and CSS since they form the foundation of web development. HTML enables you to add content to a webpage, and CSS lets you style that content.
Topics related to HTML/CSS that often appear in interviews and are directly relevant to practical work include:
- Defining HTML.
- Explaining the CSS Box Model.
- Benefits of CSS pre-processing (understanding its usage at a basic level and its advantages for developers).
- CSS Media Queries targeting different devices and providing corresponding CSS.
- Bootstrap (a framework aiding in designing and layout on a webpage). While many programs focus on teaching Bootstrap, fundamental CSS knowledge is more crucial than specific Bootstrap features and methods.
2.2. JavaScript
JavaScript has become increasingly popular over the years, with new libraries, frameworks, and tools continually emerging. According to the Stack Overflow Developer survey, JavaScript is the most popular language in Full-Stack, Front-end, and Back-end development.
Here are some topics you need to understand to become a Full-Stack Developer:
- Working with the Document Object Model (DOM), understanding JSON and its application.
- Essential language features: functional composition, prototypal inheritance, closures, event delegation, scope, higher-order functions.
- Handling asynchronous control, promises, async/await, and callbacks.
- Properly structuring and modularizing your code, utilizing tools like webpack, browserify, or build tools such as gulp.
- Familiarity with at least one popular framework (going beyond just learning a library or specific framework features; deep JavaScript understanding makes approaching frameworks less challenging).
- While opinions on using or avoiding jQuery code vary, knowing jQuery can be helpful as it still exists in many applications.
- Basic knowledge of testing frameworks and their significance.
- Familiarity with important ES6 features.
2.3. Back-End Language

Once you're comfortable with HTML/CSS and JavaScript, you'll want to delve into a back-end language to handle tasks like database operations, user authentication, and application logic.
While most online training and bootcamps focus on specific back-end languages, it's perfectly fine to learn more than one language as long as you understand the underlying concepts and essence of the language.
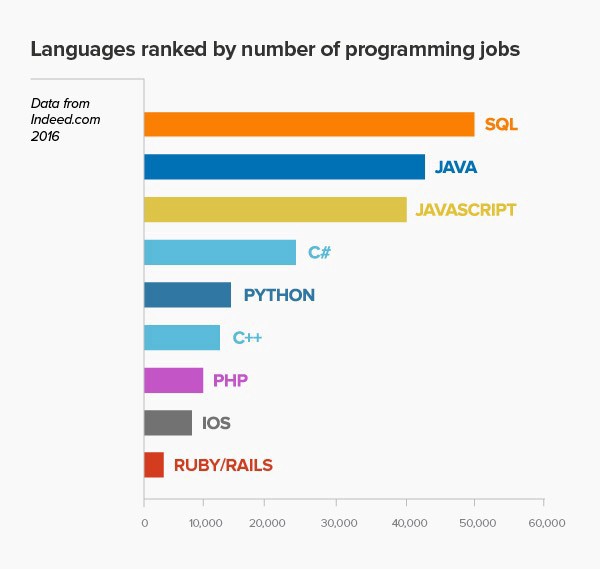
Here are a few popular back-end language options:
- Node.js: Node.js is a great choice because it's a JavaScript runtime environment, eliminating the need to learn a new language. Express is a popular framework that can assist in web application development using Node.js.
- PHP: PHP is widely used in Vietnam and many IT companies for large-scale production. Laravel is the most famous and beginner-friendly PHP framework.
- Ruby: Ruby has frameworks like Rails and Sinatra. Ruby is often taught as an introductory back-end language.
- Python: Python has frameworks like Django and Flask.
- Java: While Java might not be as frequently taught in Full-Stack Web Development programs, it's still essential and used by some companies. It's crucial to learn and understand Java.
The choice of a back-end language can elicit varying opinions, but what matters most is committing to learning and understanding your chosen language.
2.4. Databases & Web Storage

When learning to build web applications, there might be cases where you need to store data somewhere for future use. It's important to grasp the following topics related to databases and storage:
- Understand the benefits of relational data, e.g., MySQL.
- Learn about NoSQL databases, e.g., MongoDB.
- Understand when to use each in specific situations.
- Know how to connect databases to the back-end language you've chosen (e.g., Node.js + MongoDB).
- Understand the advantages of in-memory databases like Redis or memcached.
- Utilize web storage to store sessions, cookies, and cached data in the browser.
- Understand database scaling, ACID principles, and ORM (all optional).
2.5. HTTP & REST
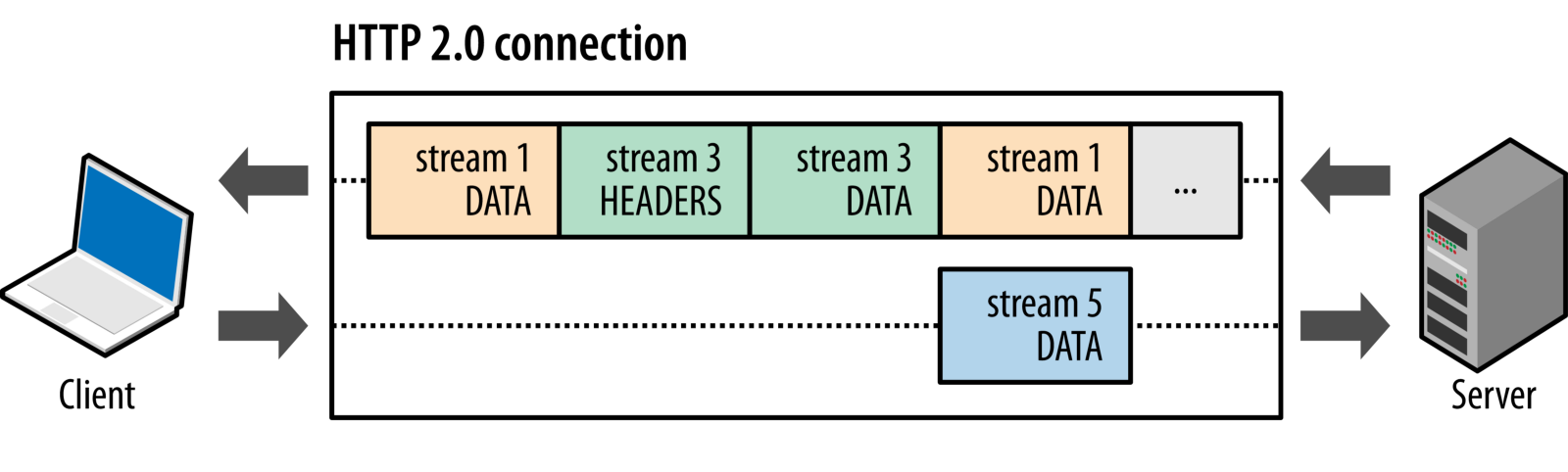
HTTP is a non-text application protocol on the Internet – it enables clients to communicate with servers (e.g., your JavaScript code can request AJAX to execute some back-end code on a server via HTTP). Some important topics to learn include:
- Understanding REST and its significance in the HTTP protocol and web applications.
- Best practices for designing RESTful APIs, POST / GET requests.
- Familiarity with Chrome DevTools can be highly beneficial.
- What is an SSL certificate?
- HTTP/2 & SPDY (optional), WebSockets, Web Workers, and Service Workers (all optional).
2.6. Web Application Architecture
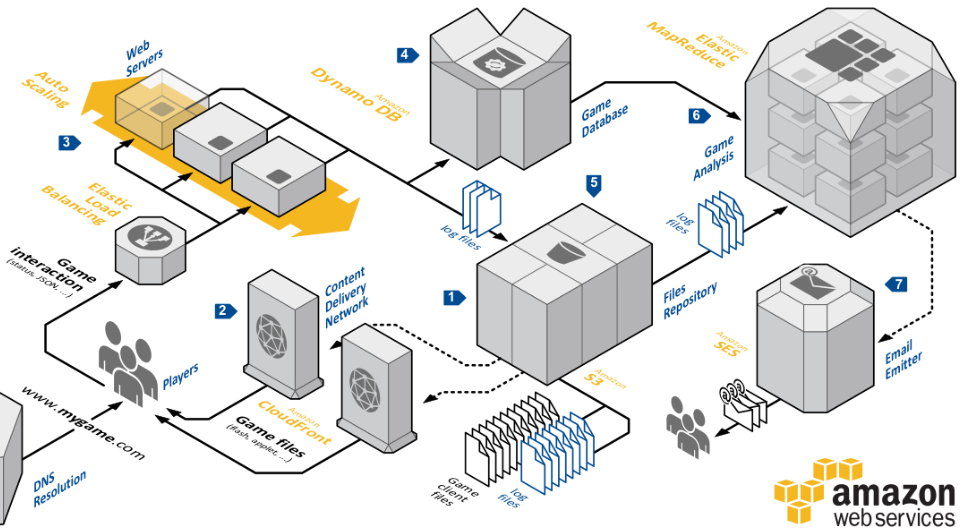
Once you feel confident in HTML/CSS, JavaScript, back-end programming, databases, and HTTP/REST, the next step is more challenging. At this point, if you want to create complex web applications, you need to understand how to structure your code, separate files, store large files, organize data in your database, determine where to perform certain computations (client-side vs. server-side), and much more.
It's essential to engage in hands-on projects and work with a group to develop a large, intricate application. This practical experience enhances your ability to design and structure applications effectively.
2.7. Git

Git is a version control system that allows developers to work collaboratively on a project and track changes to the codebase. Basic Git knowledge is necessary to stay updated with the latest code changes, update portions of code, fix issues, and modify others' code without breaking anything. It's recommended to understand the underlying principles of Git and practice using it.
- Common Git commands to use.
- Guide to using Git and GitHub for beginners.
2.8. Basic Algorithms and Data Structures
This topic is polarizing in the programming world. Some developers believe that topics like tree traversal, sorting, algorithm analysis, matrix operations, etc., should not be heavily emphasized in web development. However, many companies seek candidates with computer science degrees or equivalent qualifications.
To become a senior full stack developer, it's important to have a solid grasp of basic algorithms and data structures. This knowledge minimizes code redundancy and improves system performance. Here are some key points to learn:
- Hash tables and deep understanding, as they underlie objects in JavaScript (dictionaries in Python, hashes in Ruby).
- Familiarity with tree and graph structures.
- Basics of Big-O analysis to avoid common pitfalls.
- Knowing when to use an object with an array and understanding balance.
- Understanding the importance of caching with large datasets and the pros and cons of in-memory and external memory.
- Differentiating between queues and stacks.
Learning all of this might be challenging, but the ultimate reward is well worth it. Best of luck on your journey to becoming a successful developer! Jung Talents wishes you success!